Phone: 8613421351153
Characteristics of Fireproofing of Flat Profile Composite Floor Slabs
Illustrate:
The main purpose of fire protection is to protect life safety while minimizing property and economic losses. These purposes can basically be achieved by the following methods:
(1) Minimize the risk of ignition.
(2) Provide safe escape routes and exits for the public.
(3) Limit the spread of fire.
(4) Minimize the risk of possible collapse of the structure after fire.
Due to the closed rib cross-section design of the flat profile composite floor slab, the composite floor slab provides a fire barrier with a uniform thickness of concrete. When the bottom of the slab is burned by fire, except for the direct exposure of the trough slab, it will be regarded as useless steel, the rest of the slab ribs completely covered by concrete, their temperature changes are similar to the temperature changes of the steel bars in the cast-in-place concrete slab under different thicknesses of the protective layer, and they are still quite competent to resist the positive bending moment steel bars, so the flat profile composite floor slab combination The fire-resistant design performance of the floor slab (whether it is thermal insulation, integrity and structure) is obviously not comparable to that of other types (W profile or Re-entrant-trough profile) composite floor slabs.
Composite floor slab design without fire protection:
Rule 1: Minimum thickness of floor slabs
According to the British national standard BS5950Part8:section8.9, when the steel deck composite floor slab is not protected by fireproof materials at the bottom of the slab, the minimum thickness of heat insulation that the floor must have is clearly defined, as shown in the following table:
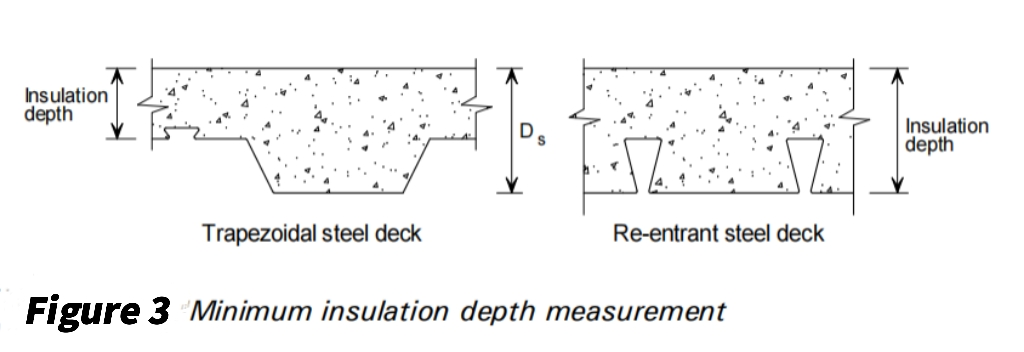
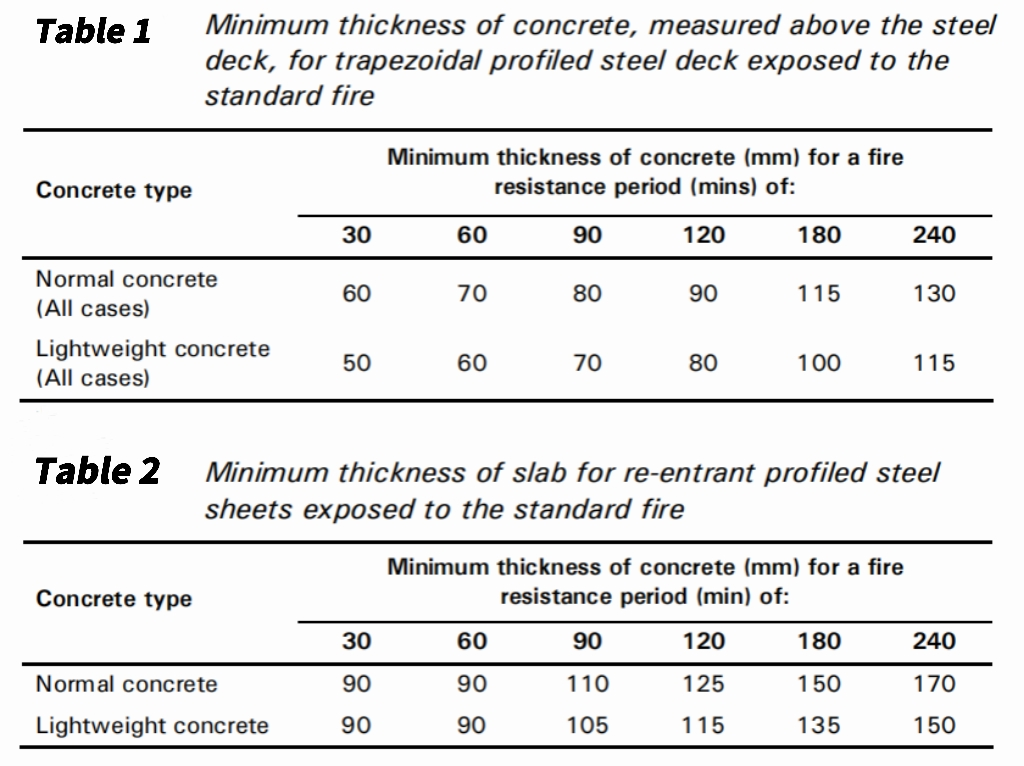
According to the temperature detection test and the fire resistance test results under load conditions, it shows that the heat insulation of Solideck’s SD65-555 and SD66-720 composite floor slabs is significantly better than that of W profile or Re-entrant-trough profile slabs. When selecting the minimum floor thickness required for Solideck’s composite floor slabs, it is more than enough to refer to the relevant regulations on the composite floor of the shrinking plate.
After comparison, the final temperatures of the individual exposure depths of the above-mentioned profiled plate groove ribs are all lower than the British National Standard BS 5950 Part8 on the relative exposure of concrete components.
Criteria for temperature propagation at depth and fire resistance limit. <see table below>
Rule 2: Determination of the final temperature of the steel deck
(BS 5950:Part 8:Section 8.9.9.2-Table 12)
Temperature distribution through a composite floor slab with steel deck
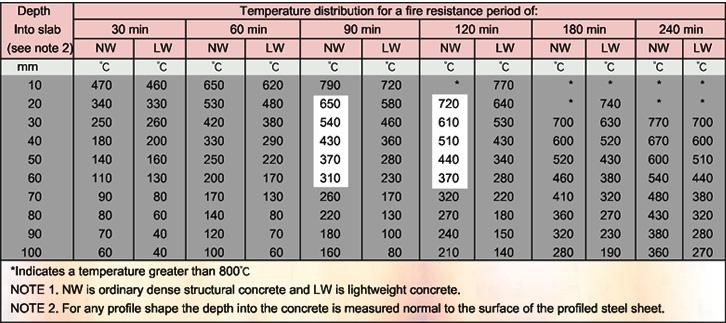
Nevertheless, for the sake of conservatism, the final temperature of individual exposure depths will still refer to the standard temperature distribution table of BS 5950 Part8 under different fire resistance limit conditions. <meaning a higher temperature value>